 |
Morsecode
|
Funktionsweise und Beispiel
The Morse Code, sometimes also named Morse Alphabet, is a method used to transmit letters and numbers.
In order to do this a constant signal is switched off and on resulting in a binary code.
This code can be transmitted as an acoustic signal, a radio signal or an electric pulse created by a morse key via a telephone line.
Alternatively it can also be transmitted mechanically or optically (e.g. by a blinking light).
Generally this code can be transmitted by every media which allows two clearly discriminable states and where it can be varied in length. This is called Morse Telegraphy.
The visualisation of this code uses sequences with three symbols, which are called "dots"(.), "dashes"(-) and "pause"( ). In short notation they are also named "dis"(.) and "dahs"(-).
The length of a "dis" characterizes the maximum transmission rate and therefore defines the basic time unit.
Below you will find an example:
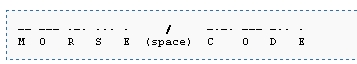
Source: Wikipedia
Bedienung
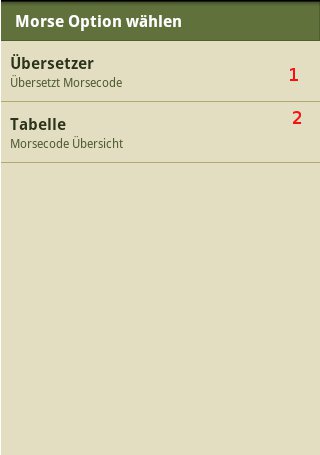
Eingabe
-
Morse Code Translation
-
Morse Alphabet Table
Ausgabe
Morse Code Translation
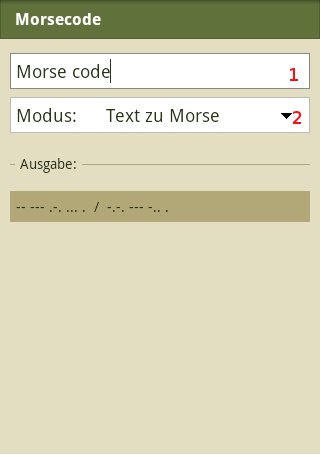
Eingabe
-
Message text to be converted
-
Selection of working mode (Morse-to-Text or Text-to-Morse)
-
Buttons for typing the Morse Code (short, long, next letter, Pause) (These buttons are only visible in "Morse-to-Text"-mode)
Ausgabe
Clear text or Morse Code
Morse Code Table

Eingabe
-
Ausgabe
Table of Morse Codes



